Please use recursive function. 請使用遞迴函數
In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers or Fibonacci sequence are the numbers in the following integer sequence: 0,1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34,55,89,144
前13的斐波那契數列:0,1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34,55,89,144
By definition, the first two numbers in the Fibonacci sequence is 0 and 1, and each subsequent number is the sum of the previous two. In mathematical terms, the sequence Fn of Fibonacci numbers is defined by the relation 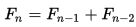 with seed values F0 = 0, F1= 1
with seed values F0 = 0, F1= 1
斐波那契數由0和1開始,其後的數就由之前的兩個數相加。用數學表示 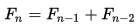 F0 = 0, F1 = 1
F0 = 0, F1 = 1
Write a program that asks the user to type an integer n, then display Fn on the screen.
寫一個輸入一個整數n,輸出第n個斐波那契數的程式
Example input 1:
5
Example output 1:
5
Example input 2:
12
Example output 2:
144